
Cisco Training Courses
Insoft has been serving IT community with official Cisco training offering since 2010. Find all the relevant information on Cisco training on this page.
View More
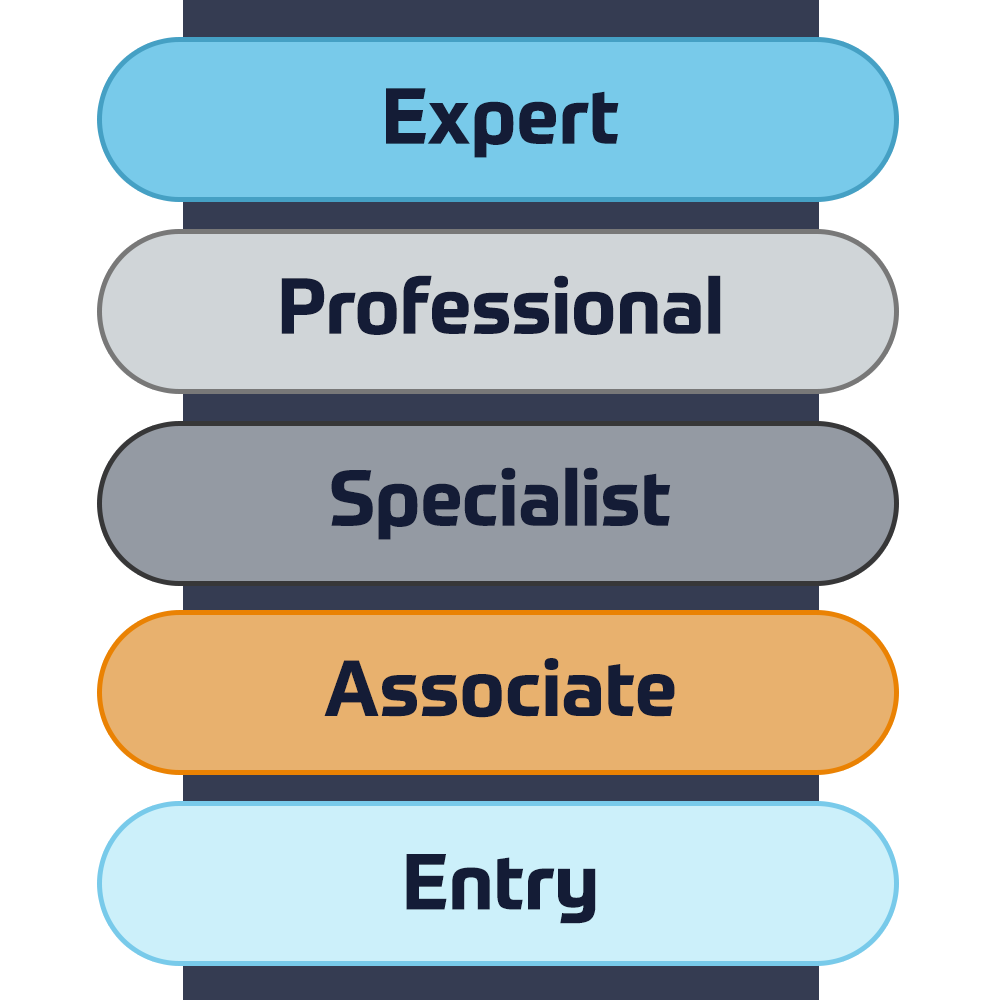
Cisco Certifications
Experience a blended learning approach that combines the best of instructor-led training and self-paced e-learning to help you prepare for your certification exam.
View More

Cisco Training Catalogue
Explore a wide variety of the Cisco courses, across different countries as well as online courses.
Browse Catalogue

Cisco Learning Credits
Cisco Learning Credits (CLCs) are prepaid training vouchers redeemed directly with Cisco that make planning for your success easier when purchasing Cisco products and services.
Have CLCs and want to redeem them?

Cisco Continuing Education
The Cisco Continuing Education Program offers all active certification holders flexible options to recertify by completing a variety of eligible training items.
View More

Cisco Digital Learning
Certified employees are VALUED assets. Explore Cisco official Digital Learning Library to educate yourself through recorded sessions.
Browse CDLL Catalogue

Cisco Business Enablement
The Cisco Business Enablement Partner Program focuses on sharpening the business skills of Cisco Channel Partners and customers.
View More
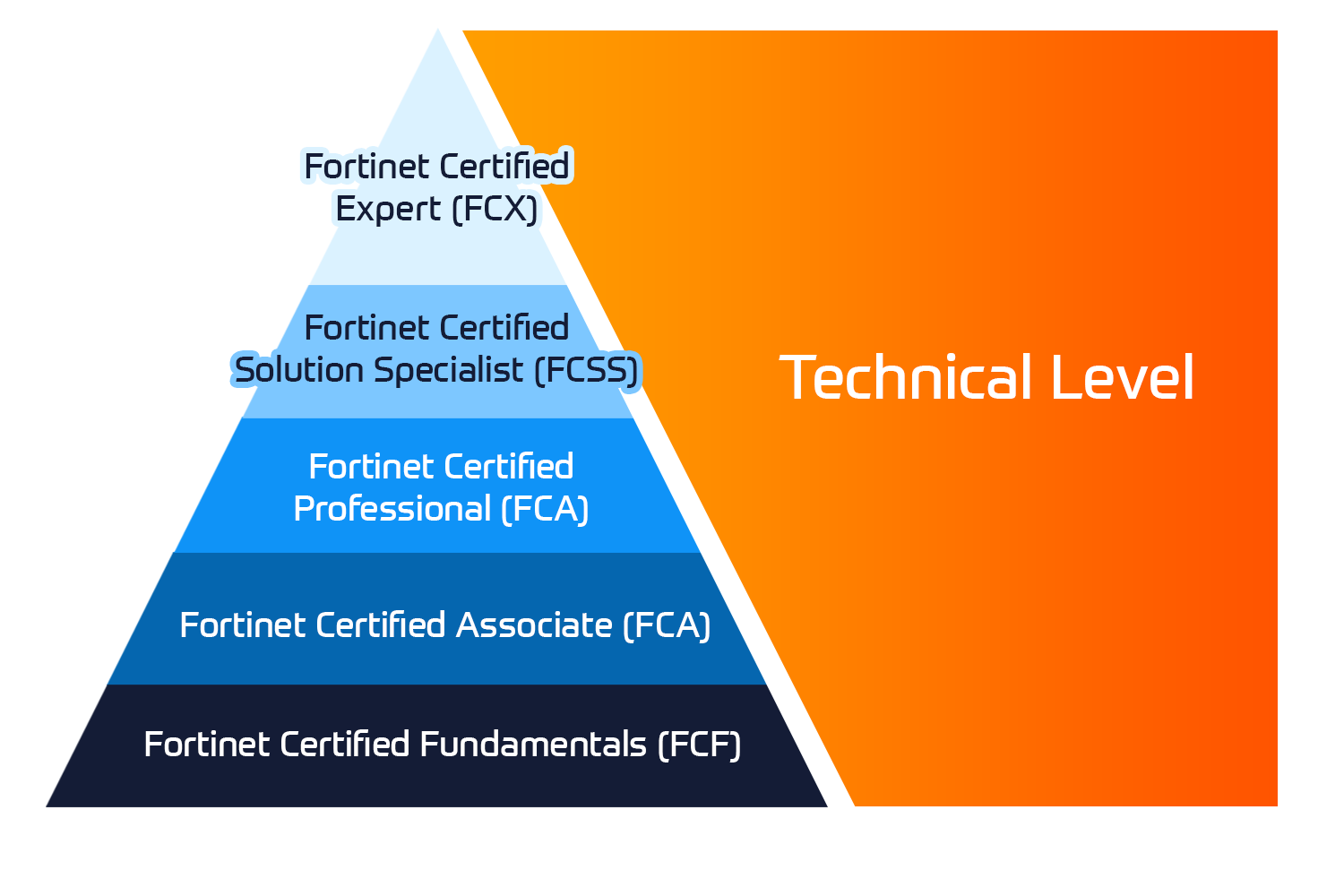
Fortinet Technical Certifications
The Fortinet Network Security Expert (NSE) program is an eight-level training and certification program to teach engineers of their network security for Fortinet FW skills and experience.
View More

Fortinet Technical Courses
Insoft is recognised as Fortinet Authorized Training Center in selected locations across EMEA.
View More

Fortinet Training Catalogue
Explore the full Fortinet training catalogue. The program includes a wide range of self-paced and instructor-led courses.
Browse Catalogue
Fortinet Services Packages
Insoft Services has developed a specific solution to streamline and simplify the process of installing or migrating to Fortinet Products.
Browse Packages

Prepforce Bootcamp
The only comprehensive source available today to prepare for Fortinet NSE 8 certification globally.
View More

Microsoft Training
Insoft Services provides Microsoft training in EMEAR. We offer Microsoft technical training and certification courses that are led by world-class instructors.
View More

Technical Training
The evolution of Extreme Networks Technical Training provides a comprehensive progressive pathway from Associate to Professional accreditation.
View More

Technical Certification
We provide comprehensive curriculum of technical competency skills on the certification accomplishment.
View More

Courses Catalogue
Find all the Extreme Networks online and instructor led class room based calendar here.
View More

ATP Accreditation
As an authorised training partner (ATP), Insoft Services ensures that you receive the highest standards of education available.
View More

Consulting package
We provide innovative and advanced support for designing, implementing and optimising IT solutions. Our client-base includes some of the largest Telcos globally.
Solutions and services

About Us
Our training portfolio includes a wide range of IT training from IP providers, including Cisco, Extreme Networks, Fortinet, Microsoft, to name a few, in EMEA.
View More
Contact Us
We would love to hear from you. Please complete this form to pre-book or request further information about our delivery options.

 Germany
Germany Denmark
Denmark Norway
Norway Sweden
Sweden Italy
Italy Netherlands
Netherlands Finland
Finland








 Duration
Duration
 Delivery
Delivery  Price
Price